Skip to main content
Getting error "Network path Not found" after running dir command from Windows NFS client
Weird Problem with Virtual PC 2007
Had a weird problem with Virtual PC 2007 where the blue screen would flash up when I ran the program, yet the console window would not appear even though Virtual PC was running in the task manager and the system tray. The Virtual PC console had effectively disappeared. All this was bad enough, but this happened to me when I was visiting a customer site and just about to demo some cool new features of SQL Server 2008 ! I had even checked my demos before setting out that morning, so this was very weird (and not to mention embarrassing) ! After uninstalling and reinstalling and scratching my head for a while, I came across the solution here...
https://www.essjae.com/blog/default.asp?id=43
Windows Failover Clustering Overview
The host node in the failover cluster performs a "looks alive" check every 5 seconds. An IsAlive check is performed every 60 seconds using SELECT @@SERVERNAME. If this fails the IsAlive retries 5 times and then attempts to reconnect to the instance of SQL. If all fail, then the SQL Server resource fails. Depending on the failover threshold, configuration of SQL resource, Windows Clustering will either attempt to restart on same node or failover to another available node.
During failover, Windows Clustering starts the SQL Server service for that instance on the new node, and goes through the recovery process to start the databases. After the service is started and the master database is online, the SQL Server resource is considered to be up. User databases will then go through the normal recovery process: any completed transactions in the t-log are rolled forward, and any incomplete transactions are rolled back. The length of the recovery process is dependent on how much activity must be rolled forward or rolled back upon startup.
Set the recovery interval of the server to a low number to avoid long recovery times and to speed up the failover process. SQL Server generates automatic checkpoints based on the "recovery interval" setting. Long running transactions can lead to much longer restart times than specified in the recovery interval option.
Failover/Failback Strategies
The cluster group containing SQL Server can be configured for automatic failback to the primary node when it becomes available again. By default, this is set to off.
To Configure:
- Right-click the group containing SQL Server in the cluster administrator, select 'properties' then 'failback' tab.
- To prevent an auto-failback, select 'Prevent Failback', to allow select 'Allow Failback' then one of the following options:
- Immediately: Not recommended as it can disrupt clients
- Failback between n and n1 hours: allows a controlled failback to a preferred node (if it's online) during a certain period.
Configure Node Failover Preferences
When you use more than 2 nodes, it's important to consider which nodes should own resources in the event of a failover. For example, in an n+1 configuration, each SQL Server group should have the idle node second in the list of preferred owners. N.B. Do not use cluster admin to remove nodes from the resource definition. USe SQL Server setup for that functionality.
To Configure:
- Right-click SQL Server group in the cluster administrator and select properties
- On the 'General' tab, the preferred owners list box contains all cluster nodes that can potentially own resources in that group, and the current order in which they will failover
- Click 'Modify' to change this order
Configure Thresholds for a Resource
- Right-click the cluster resource and then select 'Propereties'
- Click 'Advanced'
- Select 'Do not restart' if the cluster service should not attempt to restart. Restart is the default
- If 'Restart' is selected:
- Affect the Group: uncheck to prevent a failure of the selected resource from causing the SQL Server group to failover
- Threshold: number of times the cluster service will attempt to restart the resource, and period is the amount of time in seconds between retries
- Do not modify the 'LooksAlive' and 'IsAlive' settings
- Unless necessary, do not alter the 'Pending Timeout'. This is the amount of time the resource is either in the online or pending or offline pending states before the the cluster service puts it in either offline or failed state
Configure Thresholds for a Group
- Right-click the group containing the SQL Server virtual server then click properties
- Click the failover tab
- to configure the failover policy, in the threshold box enter the number of times the group is configured to failover within a set span of hours. In the period box, entrer the set span of hours
- Once the resource group reaches the set number of failovers, it will stay offline. However, other cluster resources, such as cluster IP, could be left online
Cluster Resource Dependencies
| Resource | Dependency |
| SQL IP Address (Virtual Server Name) | NONE |
| SQL Network Name (Virtual Server Name) | SQL IP Address |
| SQL Server | Disk Resource(s),SQL Network Name |
| SQL Server Agent | SQL Server |
| SQL Server Full Text | Disk Resource(s) |
| Analysis Services (2005 only) | Disk Resource(s),Network Name |
Cluster Heartbeat
Cluster nodes use the "heartbeat" signal to check whether each node is alive at both the OS level and SQL Server level. The node hosting the SQL Server resources uses the Service Control Manager to check every 5 seconds whether the SQL Server service appears to be running. This "LooksAlive" check does not impact performance but does not perform a thorough check; the check will succeed if the service appears to be running even though it might not be operational. As a result, a deeper check must be performed; this "IsAlive" check runs every 60 seconds.
IsAlive:
- Runs every 60 seconds
- Runs an @@SERVERNAME T-SQL query against SQL Server to determine whether the server can respond to requests
- Does not gaurantee that all user databases are available or are performing within necessary performance/response-time requirements
If IsAlive Check fails:
- Retried 5 times and then it attempts to reconnect to the instance of SQL Server
- If all 5 retries fail, the server resource fails
- Depending on the failover threshold config, the failover cluster will either restart the resource on the same node or it will failover to another available node
The IsAlive query tolerates a few errors, but ultimately it fails if it's threshold is exceeded
During failover of the SQL Server instance, SQL Server resources start up on the new node and SQL Server goes through the recovery process to restart the databases. After the service is started and the master database is alive, the SQL Server resource is considered to be up. User databases will go through the normal recovery process. Completed transactions in the transaction log are rolled forward (the Redo phase), incomplete transactions are rolled back (the Undo phase).
In SQL Server 2005 Enterprise Edition, each user database is available to the user once the Redo phase is complete. For all other editions (and all 2000 editions), each user database is unavailable until the Undo phase completes. Length of recovery process depends on how much activity needs to be rolled forward or back upon startup.
The 'recovery interval' sp_configure option of the server can be set to a low number to avoid longer Redo recovery times and to speed up the failover process. Undo recovery time can be reduced by using shorter transactions so that uncommitted transactions do not have much to roll back.
Recommended Heartbeat Configurations
- Two or more independent networks must connect the nodes of the cluster to avoid a single point of failure
- Use of 2 LAN's is typical (MS PSS does NOT support the config of a cluster with nodes connected by only one network)
- At least two of the cluster networks must be configured to support heartbeat communications between the cluster nodes to avoid a single point of failure
- To do so, configure the roles of these networks as either "Internal Cluster Communications Only" or "All Communications" for the cluster service
- Typically, one of these networks is a PRIVATE INTERCONNECT dedicated to internal cluster communication.
- Each cluster network must fail independently of all other cluster networks.
- The cluster networks must not have a component in common that can cause both to fail simultaneously.
- The use of a multiport network adapter, for example to attach a node to two cluster networks would not satisfy this requirement in most cases as the ports are not independent
- Remove all unnecesary network traffic from the network adapter that is set to INTERNAL CLUSTER COMMUNICATIONS ONLY (also known as the "heartbeat" or "private" network adapter, to eliminate possible communication issues
- Clustering communicates using Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) on IP sockets with User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets
Recommended Configuration for Private Adaptor in Windows 2000 and Windows 2003
Windows Memory (PAE/AWE/3GB)
PAE (Physical Address Extension)
PAE is the added ability of the IA32 processor to address more than 4GB of physical memory. The following OS's can use PAE to take advantage of physical memory beyond 4GB:
- Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server
- Microsoft Windows 2000 Datacentre Server
- Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition
- Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacentre Edition
To enable PAE, use the /PAE switch in your server's boot.ini file.
N.B. In Windows Server 2003, PAE is enabled automatically if your server is using hot-add memory devices.In all other cases, you must add the /PAE switch to boot.ini
Typically, a process running under Windows 2000 or Windows 2003 can address up to 2GB of memory address space (3GB if the /3GB switch is used in boot.ini) with some of the memory being physical memory and some being virtual. The more programs (and therefore, more processes) you run, the more memory you commit up to the full 2GB of address space. When this occurs, the paging process increases dramatically and performance may be negatively affected.
Windows 2000 and 2003 memory managers use PAE to provide more physical memory to a program. This reduces the need to swap the memory of the page file and results in increased performance. The program itself is not awareof the memory size, the memory management and allocation of the PAE memory is handled by the memory manager independently of the programs that run.
When the /3GB switch is used is conjunction with the /PAE switch, the OS does not use any memory in excess of 16GB. This is caused by kernel virtual memory space considerations. If the system restarts with the /3GB switch in boot.ini, and the system has more than 16GB available (physical memory), the additional RAM is not used by the OS. Restarting without the /3GB switch enables use of all the physical memory.
AWE (Address Windowing Extensions)
AWE is a set of API's to the memory manager's functionsthat enables programs to address more memory than is available through standard 32-bit addressing. It enables programs to reserve physical memory as non-paged memory to the program's working set of memory. Enables memory intensive programs, such as RDBMS, to reserve large amounts of physical memory for data without having to be paged in and out of a paging for for usage. Data is swapped in and out of of the working set and reserved memory is in excess of the 4GB range. Additionally, the range of memory in excess of 4GB is exposed to the memory manager and the AWE functions by PAE. Without PAE, AWE cannot reserve memory in excess of 4GB.
In Summary:
- PAE is a function of the Windows 2000 and Windows Server 2003 memory manager that provides more physical memory to a program that requests memory
- The program is not aware that any of the memory that it uses resides in the range greater than 4GB
- AWE is an API that enables programs to reserve large chunks of memory
- Reserved memory is non-pagable and is only accessible to that program
- You can't allocate more than 4GB of memory to an application on Windows Server 2000 because PAE is not available. Also cannot use the /3Gb switch in the boot.ini file with Windows Server 2000
- Need to use Windows 2000 Advanced Server or Windows 2000 Datacentre.
- PAE (36-bit physical addressing mode) allows up to 8GB of physical memory on Windows 2000 Advanced Server and 32GB on Windows 2000 Datacentre
- Maximum amount of memory supported on Windows Server 2003 is 4GB. Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition SP2 supports 64GB of physical RAM and Windows 2003 Datacentre SP2 supports 128GB. You can use the /3GB switch in boot.ini in all versions of Windows Server 2003
Memory Limits for Windows Releases
Operating Systems and PAE support
Techdays 2012 WSV303 IIS 8 簡報與範例程式檔下載
Techdays Taiwan 2012 ???????,?????? WSV303: Windows Server 2012 Internet Information Services (IIS) 8 ??????,????? IIS 8 ??????,??: ?? IP ??????????? CPU???????????????????????????????,??????????????????:
???????: https://sdrv.ms/QKYAE8
???????: https://sdrv.ms/QOLUxC
???????????????????
用 Windows Server 2012 打造 NAS (0) - 緣起
Windows Server 2012 ?????? Storage ??,???????? NAS ? OS????????????? Mini-ITX ?????????????????? NAS??????????????,??????????????? Windows Server 2012 ???????????????? Windows Server 2012 ?? NAS ???,??????????
????:
? Windows Server 2012 ?? NAS (1) - ???
? Windows Server 2012 ?? NAS (2) - ???? (Storage Space) ?
用 Windows Server 2012 打造 NAS (1) - 組裝篇
?????????,????????? WD Sentinel DX4000,?????????????????,?????????????? Windows Storage Server 2008 R2,??? Windows Server 2012 ???,?????????????
????????? NAS ?,????????????,????????????????????????????? CFI-A7879
![]()
????: https://www.chyangfun.com/products_info/mini_itx/mini_img/A7879.jpg
???????? NAS Case ?????????? NAS ??,?????????? N400 ??
![]()
????: https://www.hkepc.com/forum/attachments/month_1201/1201050008b25edba18f260a20.jpg
???????,????????????,????????:
- ??: ???? N400 NAS ??
- ??: ???? 250AB-44K ????? 80-plus ??? OEM
- ???: ???? E35M1-I (AMD APU E-350, 6 x SATA 6Gbps)
- ???: ??? 2GB DDR3 x 2
- ??:
- Intel SSD 330 120GB (OS)
- WD Green 3TB x 2
?? WD ????????????? 12,000 ??,????????? NAS ???
???:

???:


??????????

????????? Windows Storage Server 2012 ?????? NAS ???,???????? NAS ????????
???: ? Windows Server 2012 ?? NAS (2) - ???? (Storage Space) ?
用 Windows Server 2012 打造 NAS (2) - 存放集區 (Storage Space) 篇
????? Storage Space ???????? Building Windows 8 ???????? Virtualizing storage for scale, resiliency, and efficiency ??,????? RAID ??????????????RAID-0 ? RAID-1 ????????????????????,?????? RAID ????????,???? RAID ?????????????????????????? Windows Server 2012 ? Storage Space ?????????
?? Windows ????????????:?? (Disk) ???? (Volume),???????????????/?? RAID ??????,???? Fibre Channel/iSCSI ?? SAN ??? LUN????????????? (Partition),???? NTFS ??????????????????????
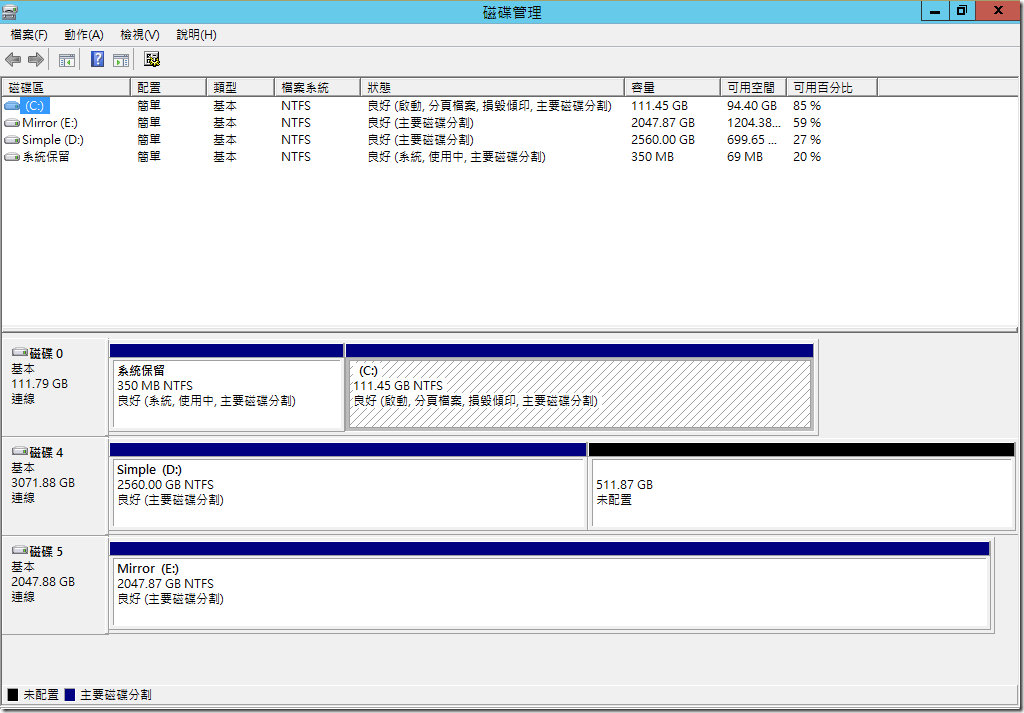
???? (Storage Space) ? RAID ?????????,???????????????????(????)??,????????????????? RAID ????????????????????? (RAID 0/1/5/10/50..),??????????????????????,?????????????????????
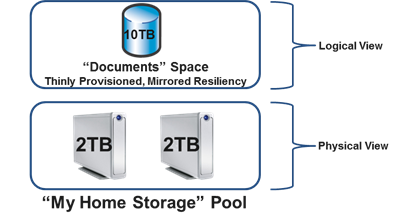
????: Virtualizing storage for scale, resiliency, and efficiency
???????????????????????,??????????? RAID-0 ? RAID-1 ??????????,????? RAID ??????????,???????????????????????? NAS ???????,????? WD Green 3T ???????????????,Simple ????? RAID-0,Mirror ????? RAID-1,????????????????????
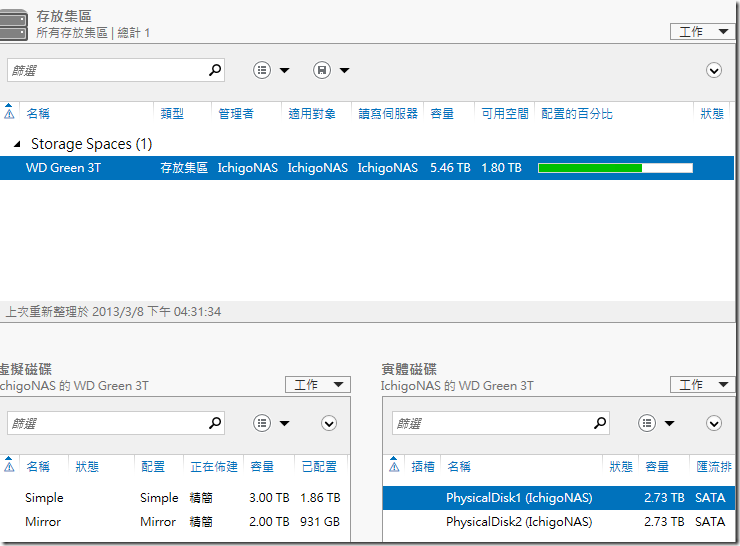
???????????????????,?????????:
- ??????
- ??????
- ??????????????????
???????,???? Windows Server 2012 ????????,?????????,?????????,??????????????,????????????? Primordial ???,???????????????????????????
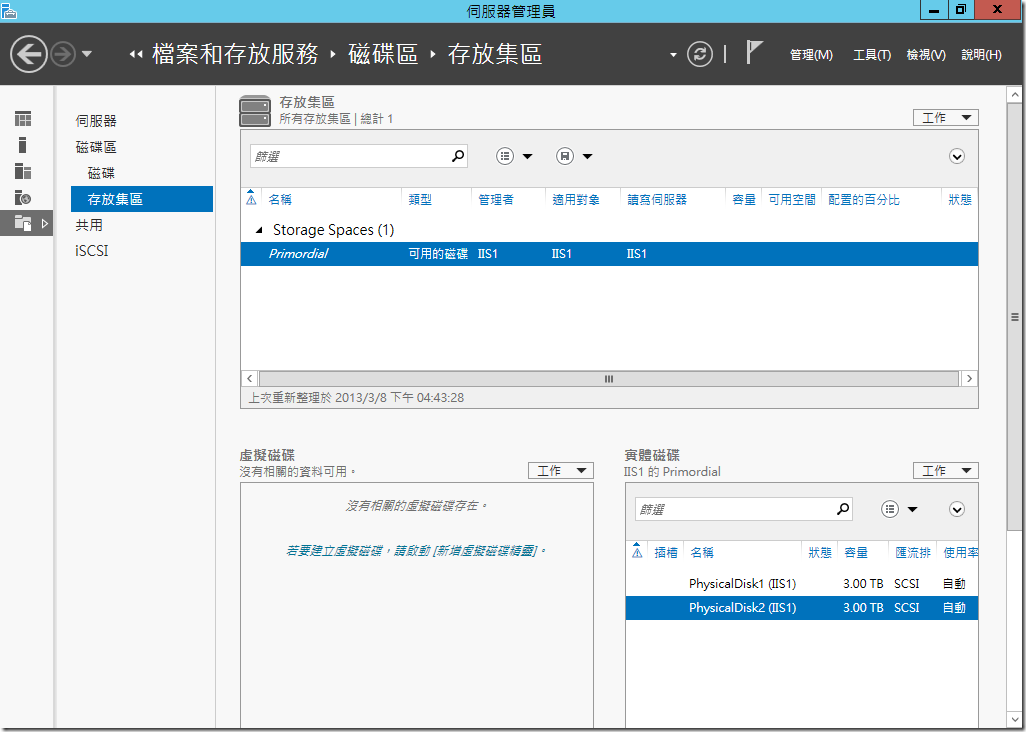
????????????????????????? Storage Spaces ??????????????????????,?????????????????,?????????????????????
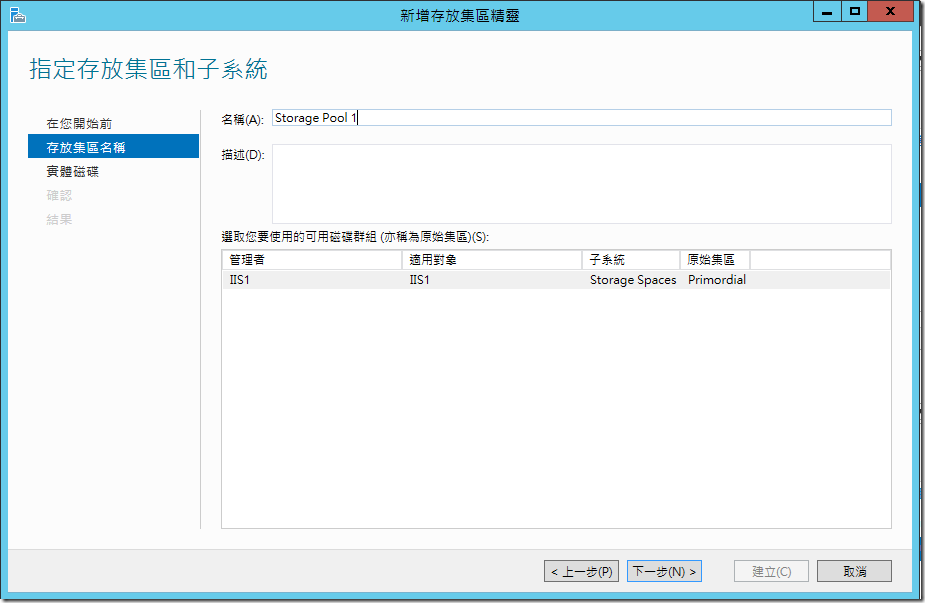
??????????????,??????????????,?????????????:?????? (Hot Spare),??????????,?????????????????????,??????????????????????????,????????????????????,??????????????????
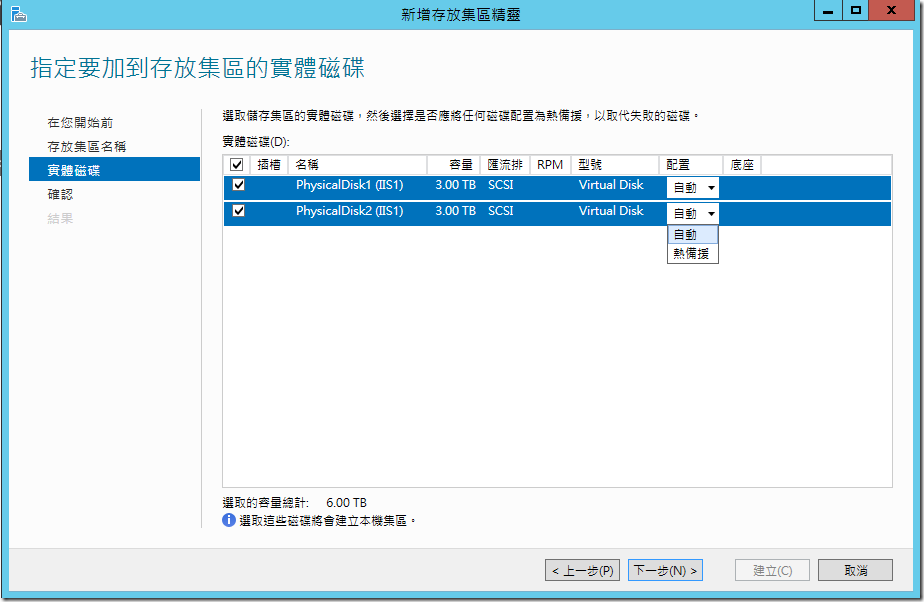
?????????????????,???????????????? 6TB ?????
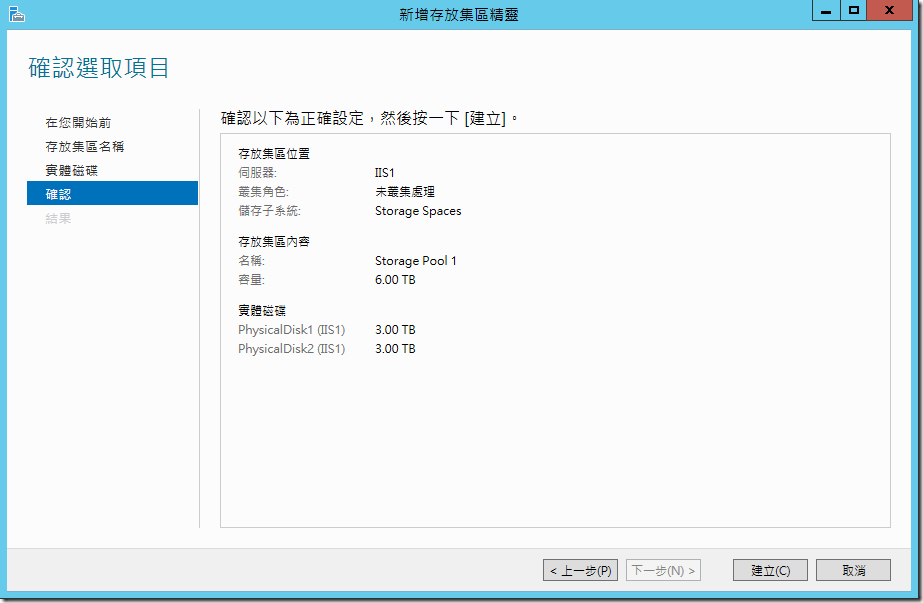
?????????,????????????:?????????????(V),?????????????????????????????
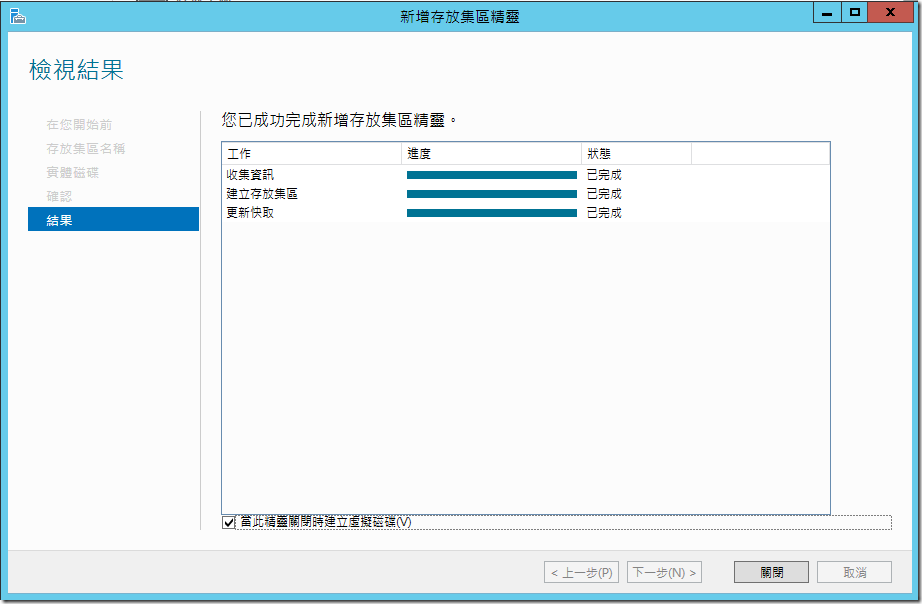
??????????,?????????????,???????????????,???????????
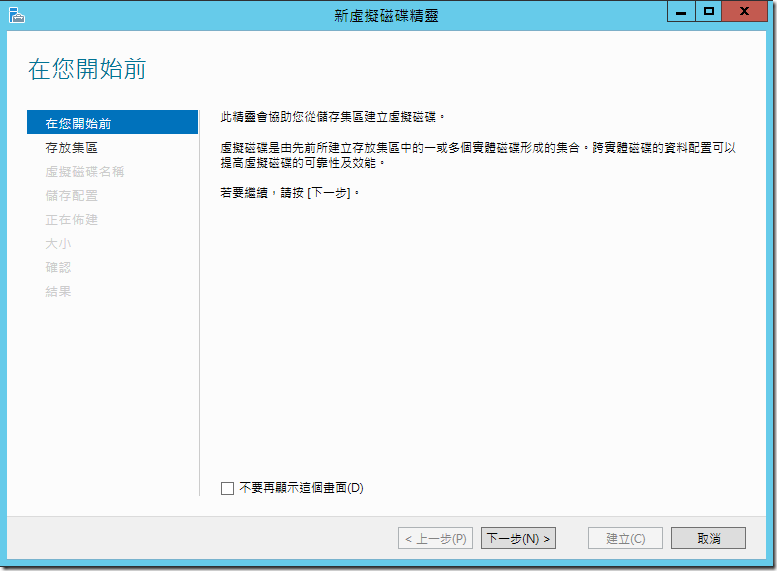
?????????????? Storage Pool 1,????????
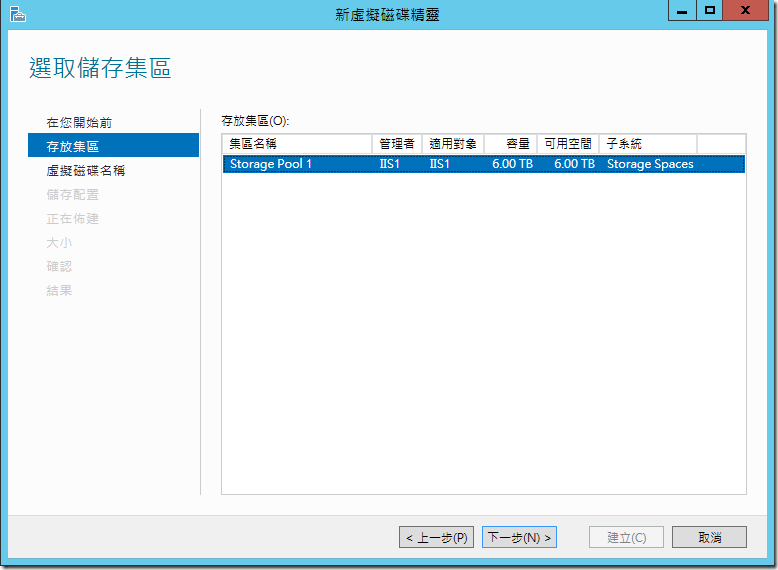
????????????,??????????????
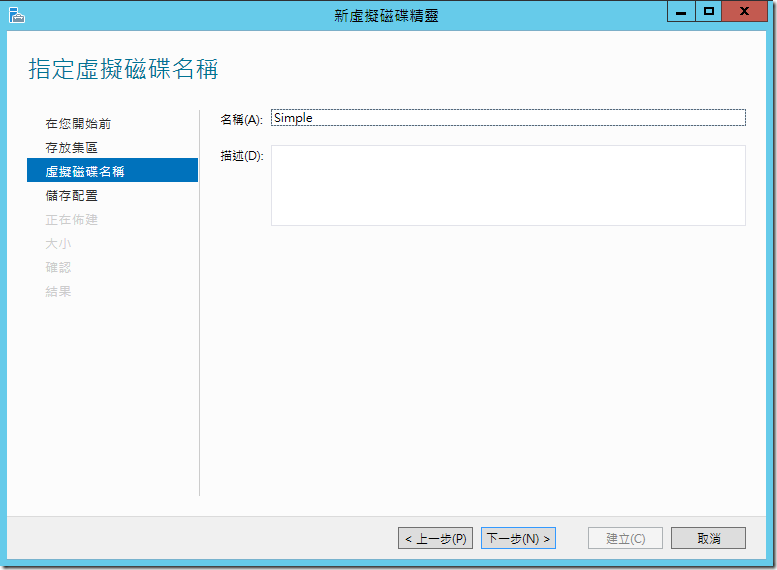
??????????,Windows Server 2012 ????????????,Simple/Mirror/Parity
- Simple: ? RAID-0 Stripe Set ??,????????????????????,?????????????????,???????????????????,???????
- Mirror: ? RAID-1 Mirror Set ??,??????????????,?????????????????,????????????(4/6/8….) ??? RAID-10 (1+0)??? Windows Server 2012 ? Mirror ??????????,????????????? 3 ????????? 3-way Mirror,??????????????,?????????????????????
- Parity: ? RAID-5 Parity Set ??,?????????? 3 ???????,?????????????? RAID-0 ???,???????
????????????????????????????,??? Simple ??
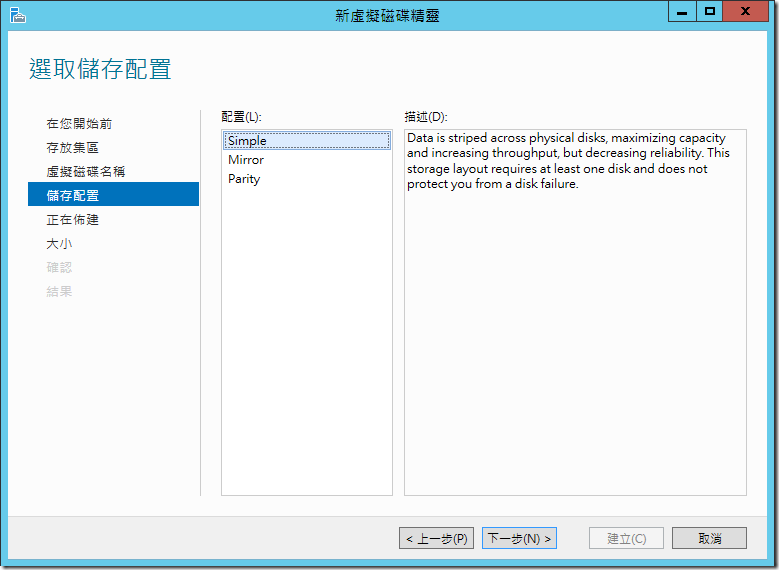
??????????,??? (Thin) ???? (Fixed) ??????????? Hyper-V ????? (VHD) ?????,???????????????????,??????????????????,???????????????????????,???? SAN/NAS ????? Thin Provisioning,??????????? Storage Virtualization????????
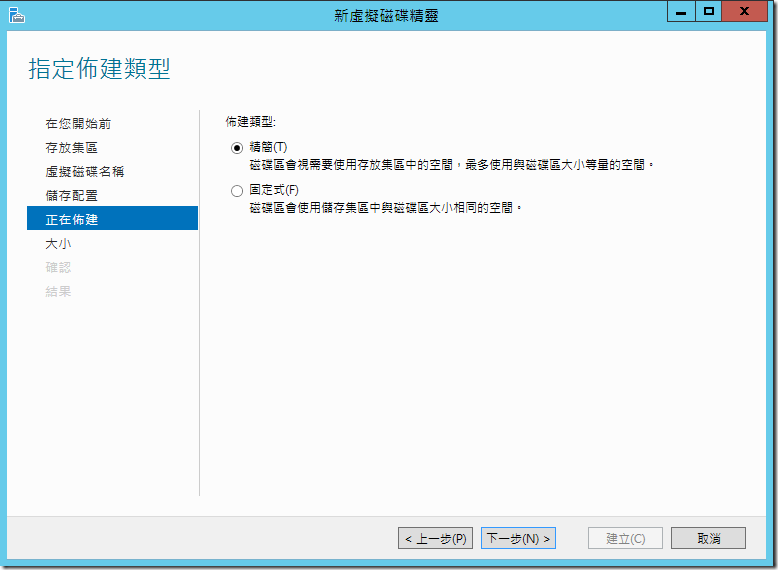
?????????????,?????????????????,??????????????? 6TB,?????????? 100TB ?????,??????? 6TB ?????????????????????????????,?????????????,???????????????????????,???????????
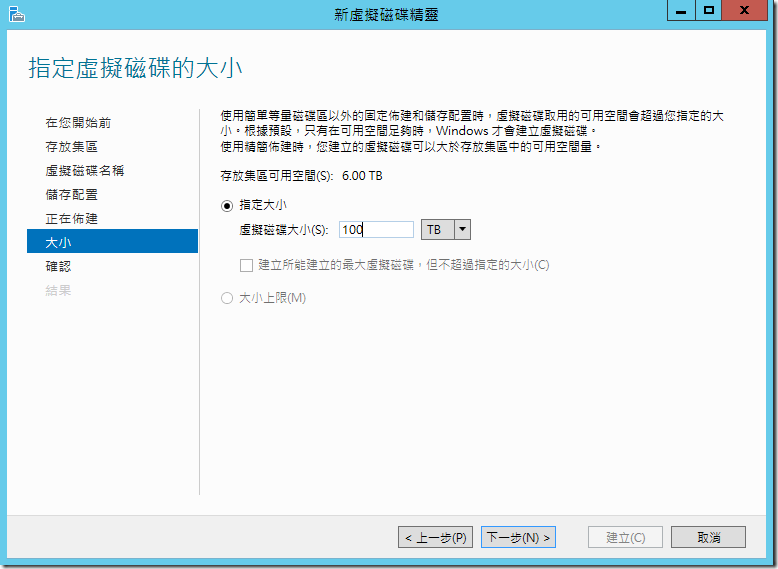
?????????????????????,???????????????
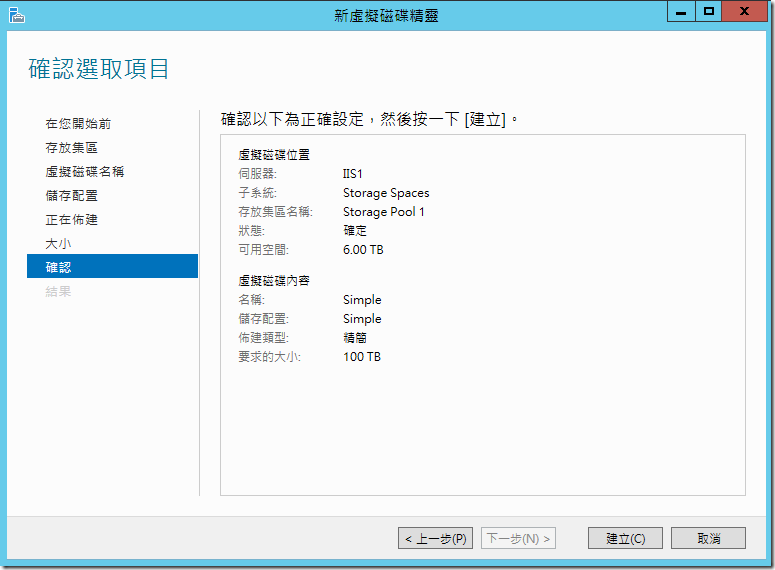
?????????????????????????????????????????????,??????????????,??????? Windows ??????????? (Partition),???? NTFS/FAT32/ReFS ????????????????????
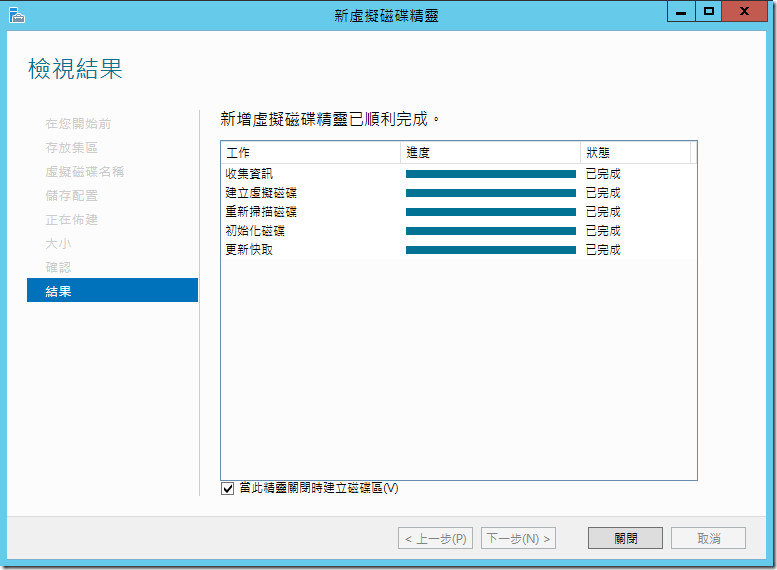
Windows Server 2012 ????????????????? NAS/File Server,?????????????????????????,?????????????? (Thin Provisioning) ????? (Simple/Mirror/Parity) ?????????????
Hello world!
Welcome to Technet. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start blogging!
AD primary group (primarygroupID) being sent by the NFS server in case of Kerberos Authentication instead of gidNumber
With Windows 2012, there are multiple options of mapping users and group for NFS access. This has been discussed on the blog below:
https://blogs.technet.com/b/filecab/archive/2012/10/09/nfs-identity-mapping-in-windows-server-2012.aspx
We came across the difference in behavior while we use the authentication type as Auth_sys to the authentication type Kerberos.
While using Kerberos as authentication type on the NFS share then the response from the NFS server is the uidNumber of the user and the primary group for the user in AD which is configured through the "memberof" tab. Hence in case of Kerberos the NFS server does not send the gidNumber set on the user's properties.
In case of Auth_sys, the NFS server sends the uidNumber and the gidNumber as the GetAttr response to the NFS clients.
I have attached Network traces for reference. Assuming the below environment, we have tested the scenario and collected the netmon traces:
Environment: Windows 2012 as NFS Server, Linux ES 6.4 as NFS client
- On the Windows NFS server, two shares are configured. Once with "Auth_sys" as authentication type.
- The other NFS share is configured with Kerberos an authentication type (Krb5,Krb5p, krb5i)
- AD lookup configured for the user with uidNumber and gidNumber
- Primary group set for the user through the memberof Tab is "DomainUsers".
Observation:
- When the user/NFS Client is authenticating by windows, it is being issued a Kerberos ticket which is being used in any create/access call by the UNIX, snapshot of the screenshot
- The Primary group of the user in the Active Directory is set to 'Domain Users' which will be put in as a Primary Group in the PAC when a Kerberos ticket is given to the user. PAC also contains the SID of the users and the groups the user is member of. The primary group is defined as "ULONG PrimaryGroupId;" in the PAC structure, see https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc237917.aspx for more details.
- When we create a file/folder from windows side, it is always setting the GID as the primary group i.e. Domain Users since this is what it finds as the primary group from the PAC while creating the token and this is always true when creating the file/folders from windows irrespective of NFS Authentication module (Krb5 or Auth_Sys).
- When we create a file/folder from NFS Client (Linux), depending upon the authentication mechanism (krb5 or Auth_sys), the GID is being sent by windows NFS Server. If we are using Kerberos authentication, then windows will consider GID as the primary group since this is what will be in the PAC. When we use Auth_Sys, since there is no PAC involved, NFS Server sends the GIDNumber configured in the AD for the user as per RFC. Looking at the SETATTR Call, the client is sending the UID and GID in the Credential structure. NFS Server will respond with the UID and GID which is configured in the Active Directory in the NFS Application layer packet (in case of Auth_Sys)
- The AUTH_SYS case differ from the Kerberos case because in the Kerberos case we get explicit information earlier in the process as a result of the Kerberos ticket and so there is no need to go further and check the gidNunber for the user.
SETATTR Call sent from the client: (Kerberos)

SETATTR Reply from the server: (Kerberos)

SETATTRCall sent from the client: (Auth_Sys)
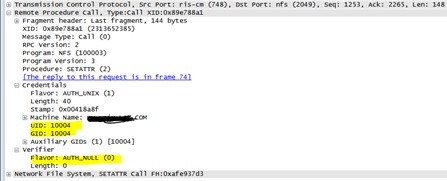
SETATTRReply from the server: (Auth_Sys)
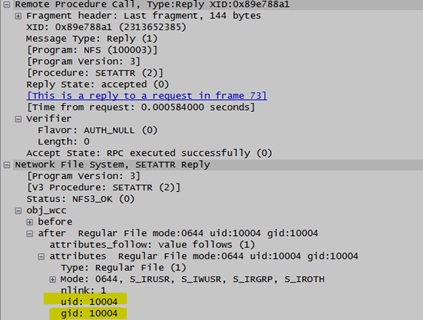
Alternate solution suggested:
- Set the Primary Group of the User from the Memberof Tab to the Unix Group (GID).
- Use the Auth_Sys authentication in the NFS Server.
- Populate the gidnumber of Domain user and
- Use the same gidnumber in the user's attribute
- Map domain user group to the Unix group
Adding NFS resource as a Network location for persistent access
Lot of times, we get request where customer are looking for having a persistent NFS mapping. Well NFS share on Windows clients are not available to all user's session. One of the recommended option would be to add the NFS resource as a Network location. The steps below describes the same.
1. Right click on computer and click on Add a Network location
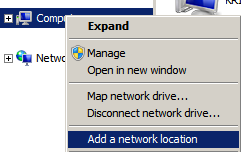
2. Click on Next
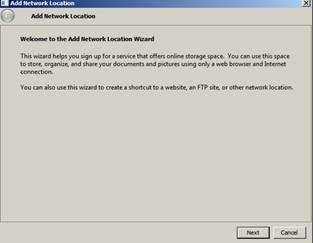
3. Click on "choose a custom network location and click Next again
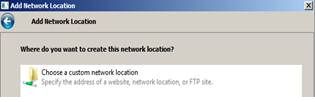
4. Put the IP address of the Unix NFS server and the share name and click Next
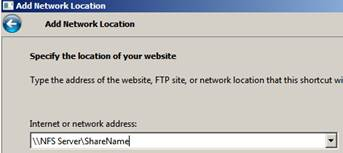
5. Then type the name (your choice). The network share will appear in the same name.
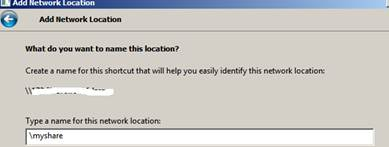
6. Then you will get the below Window: Click on Finish
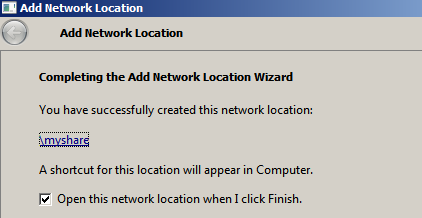
7. Once done, you should be able to access the share under your Network location.
Can we run SUA command under Windows the task scheduler ?
While working on a cron job issue, one of the customers wanted to know if they can run the SUA command through a task scheduler instead of cron job. Below are few steps which we can run from the korn/C shell on a system which has subsystem for Unix installed along with SUA SDK package.
- crontab –p ==>(enter the password for the domain user)
- crontab <cronjob file> ==> ( to run the cronjob)
- crontab –e ( to edit) ==> to edit the cronjob)
Now, regarding the question of running SUA commands through task scheduler, yes we can run it. The syntax which you need to put on a notepad is:
"c:\WINDOWS\posix.exe /u /c /bin/ksh -l -c /dev/fs/C/Windows/SUA/bin/ls > c:\test.txt"
The above command will run the 'ls' command and dump the output to C:\test.txt. Similarly, one can tweak the command as per their requirement. Once done, we need to save the notepad as somename.cmd (.cmd is a must).
The open the task scheduler (Programs ==> Accessories ==> System tools ==>Task Scheduler
The under the Actions tab, select the appropriate .cmd file and start the task schedule.
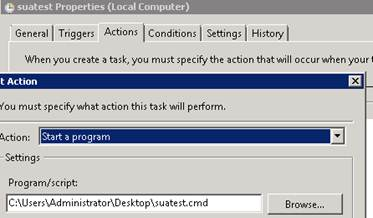
More inputs on task scheduler can be found in:
https://support.microsoft.com/kb/308569
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd851678.aspx
Character translation does not work on Windows 2012 with NFS v4.1
Character translation between Windows to Unix does not working on Windows 2012 with NFS v4.1. For NFS v3, on Windows 2012 the same configuration works.
This is because the RFC for NFS v4.0 and above is all about uniformity of file names, UTF-8 encoding etc. explicitly. Hence Character translation does not apply to v4.1 and this is now a legacy feature which is still available for NFs v2/v3.
NFS v4.1 is internationalized by the RFC definition and does not warrant any encodings – it mandates UTF-8 in all cases. Hence no additional encodings over the v4.1 protocol is required.
The GUI encoding options (e.g. SJIS, ANSI, EUC-J, etc) which we get while configuring NFS shares applies to NFs v2/v3.
Command line installation of IDMU component in Windows 2012
This article discuss on the steps required to install IDMU component using DISM on WIndows 2012. You can find more informaiton on DISM on the Blog. Looking for the GUI based installation through role and features may get complex at times. Hence this blog, discuss on the simple steps through command line to install the IDMU role on a WIndows 2012 DC.
One can run the command below through the cmdlet.
- DISM /online /enable-feature /featurename:AdminUI
- DISM /online /enable-feature /featurename:NIS
- DISM /online /enable-feature /featurename:PSync
Once done, you would need to reboot the box. Once the box is rebooted, try opening the IDMU console. It will throw an error that niscnfg.exe needs to be run.
Locate and run the niscnfg.exe executable and then also register nisprop.dll ( regsvr32 nisprop.dll). These additional steps will ensure that IDMU is configured properlly and one can start using it.
Command recall using the up arrow in Korn shell
The command below can be used on a Korn shell to use the command recall feature using the up arrow on a korn shell.
We can use 'history' command to displays a list of commands numbered in the order in which you have used them. By default the previous 128 commands which you have used are saved.
We can also the the 'r' command to rerun the previous command
Concepts on multiple user mapping
We do get a lot of questions on multiple users mapping between Windows and Unix users. I have tried to list the questions and the answers for them through this blog:
- How does multiple user name mapping works
<Answer> We can map a Windows-based account only to a single UNIX-based account, but
a single Unix based account can be mapped to multiple Windows based account.
The below support document talks more about it https://support.microsoft.com/kb/269736
2. What is Primary mapping?
<Answer> The primary mapping is used when the UNIX account or group is mapped to multiple Windows account or group. In this scenario, we set one of the Unix and Windows mapping as primary. By default, the first mapping that is created is automatically designated as the primary mapping.
For example, we have NFS shares configured on Unix box and accessing it from windows client. Then in this scenario the ownership information for the file flows as per the primary user map set.
3. What would be the recommended scenario to use multiple user\group mapping?
<Answer> Multiple user\group mapping is recommended on the scenario, where we have NFS shares hosted on Unix NFS server and we are accessing the NFS shares from Windows NFS clients (i.e the "Client for NFS" component).
For example: There is a NFS share on the Unix box which has directories owned by "UnixuserA". From the Windows box, there would be multiple users who would be accessing the
NFS share. So we mapped all the Windows users to UnixuserA . Now based on the permission set on the NFS share for UnixuserA, all the mapped Windows users will get the same permission.
However this is not recommended on the scenario, where Windows is hosting the NFS shares (i.e the "Server for NFS" component) and Unix NFS clients are accessing the files. Since we are mapping multiple Windows users to single Unix user, it may get confusing with respect to the permission flow. Also, the way user name mapping works; in case of duplicate ids; only the primary one prevails.
4. What can be done for the scenario "Server for NFS"
<Answer> So in case of Server for NFS, where the subfolder and files under the NFS shares would be owned by multiple Windows users, we can keep the setting below:
Map a single Windows user to single Unix user. On the parent NFS share make this mapped Windows user as an owner (though this is not a prerequisite) and give him the required permission. Then go to the advance security setting and under the apply to tab, select the option which says "this folder, sub folder
and files".
With this, you need to check one more registry setting, Keepinheritance under :
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Server for NFS\CurrentVersion\Mapping. This should have a value 1
More information on managing NTFS permission on a NFS share can be found on the blog below: https://blogs.technet.com/b/sfu/archive/2009/08/27/how-nfs-access-works-over-ntfs-permissions.aspx
Configuring Kerberos for NFS 4.1 access ( Ubuntu)
This blog talks about configuring Kerberos on Ubuntu for NFS access. NFS is hosted on a 2 node cluster environment.
Environment:
- Windows 2012 as DC and cluster node
- Ubuntu as NFS client
Cluster node:
- Ran the command on the cluster node to check the SPN for NFS
C:\> setspn –l node1
Registered ServicePrincipalNames for CN=node1.CN=Computers,DC=contoso,DC=local:
nfs/node1
nfs/node1.contoso.local
WSMAN/node1
WSMAN/node1. contoso.local
RestrictedkrbHost/node1
HOST/node1
RestrictedkrbHost/node1. contoso.local
HOST/node1. contoso.local
Windows 2012 DC:
- On the DC, created a container and a user called linuxclientuser
- Disabled Pre-Auth for the user and Enable AES 256 Bit encryption option
- Register the spn for the Ubuntu (NFS client) by running the command below. The command needs to be run both for the host name and the FQDN of the Ubuntu client.
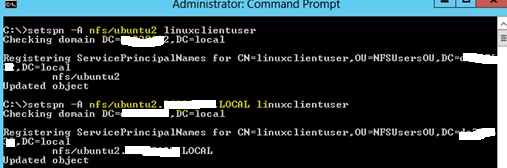
4. Ran the ktpass command to create the keytab

Note: ubuntu2.contoso.local is the linux machine host name. It is not joined to the windows domain rather only has the host (A) record in the DNS.
Note: In order to make sure AES works for the TGT, we need to raise the domain functional level to 2008 or later.
Note: We had to make a reverse lookup zone and registered the NFS Server PTR record there as linux client was constantly querying for this.
5. Exported the keytab file to Ubuntu.
Ubuntu:
1. Ran the following command on Ubuntu:
2. Referred https://help.ubuntu.com/community/NFSv4Howto for NFS v4.1
3. We need to install the below modules:
-
- apt-get install libpam-krb5
4. Run the following command
5. Add rpcsec_gss_krb5 to /etc/modules to have it loaded automatically ==> This at times get loaded automatically
6. Edit the file, /etc/default/nfs-common :
- NEED_GSSD=yes è ( this needs to be added)
7. Start the following gssd service:
8. Run the command
- kinit –k nfs/linuxclient.contoso.com ==> to make sure this has been configured properly
9. Try mounting the share using NFS v4.1 and Kerberos
mount –o sec=krb5,vers=4,minorversion=1 windowsnfsserver:/share /mnt/share
Alternativelly, you can make the changes below on the /etc/fstab file

Explorer Windows on windows NFS client freezes while access shares hosted on NetApp
Recently we got a case where the explorer window on the Windows NFS client was freezing intermittently and the unfreezing while it trying to access NFS share. The NFS share was hosted on NetApp filer and hence was a multipath.
Initially we thought that it could be an issue with the multipath NFS share, which our NFS client is not known to handle very well. During the troubleshooting, we also update the NFS and RPC related drivers. But this did not resolve the issue.
Also we found that the issue was only happening if we access the share using UNC path. Mounting the UNC path to a drive and then accessing the share had no issues. We collect network traces and NFS tracing logs and found the below:
NFS traces indicated a problem TCP ports recycling in the Client for NFS driver. While using UNC access, the Client for NFS components needs to perform the mount/unmounts sequence for every access request as the persistent connection is not available. With the "Use Reserved Ports" option turned on, the TCP port pool available to use becomes limited and it increases the likelihood of TCP ports not being available to use. In those situations, the Client for NFS component keep trying until it get a ports that it can use and that can cause the freeze that you were experiencing.
Hence we suggested to disabled the "Use Reserved Ports" option under the security option for client for NFS properties. This increased the pool of available ports to use and mapped the NFS share to a drive letter so that we don't waste CPU cycles and bandwidth with frequent mount/unmounts requests. SO, making the changes and restarting the Cleint for NFS service resolved the issue.
Fatal error (Error code: 0x80070643): Unable to installadd the NFS role services on Windows 2008 R2 server
Recently we got an issue where the customer was unable to install NFS role services on Windows 2008 R2. He was getting the error message below.
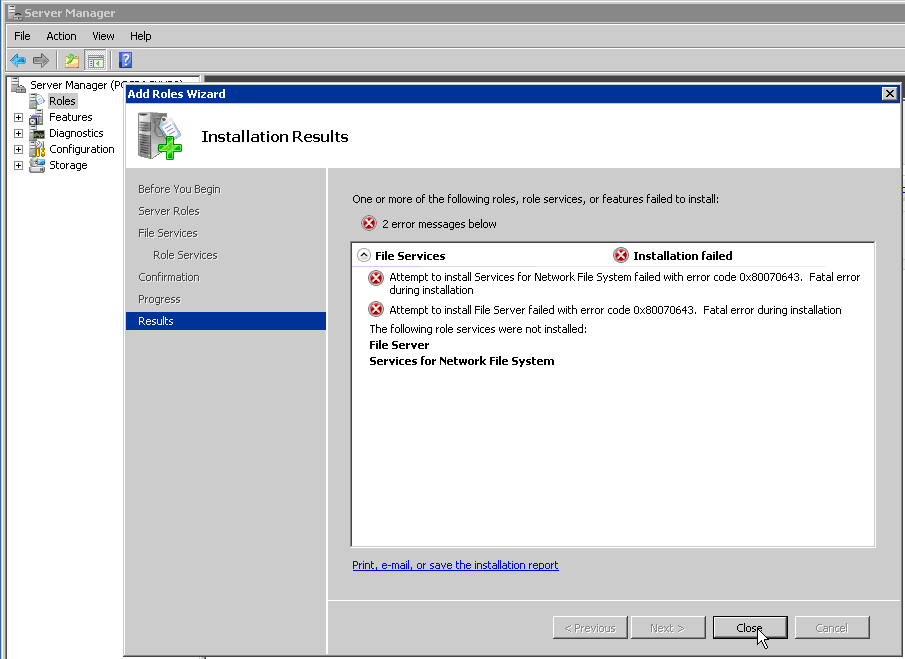
To begin with, we got the output of the command 'netstat –ano' to verify if any other service is running on port '111'. But the output did not had port '111' listed.
Customer was logged in as local Administrator account on the machine. We tried installing the component as domain admin account on the same machine. But this did not help the cause. We still got the same error.
We checked the Windows Installer service and that was not running. Starting the service also made no difference as we were still getting the same error.
Then we browse to the registry location below and found that we were unable to create any new Key.
"HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\explorer\ShellIconOverlayIdentifiers"
We verified the permission on the registry key and also tried adding the Administrator user and the domain user to this registry and gave full control. Still we were unable to create a new key and were getting permission denied.
Verified with the customer if he has any Antivirus running on his system or not. Customer informed that he has McAfee running.
We found that "McAfee's Access Protection rule" blocking the Installation by restricting the edit permission on the registry key below:
"HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\explorer\ShellIconOverlayIdentifiers"
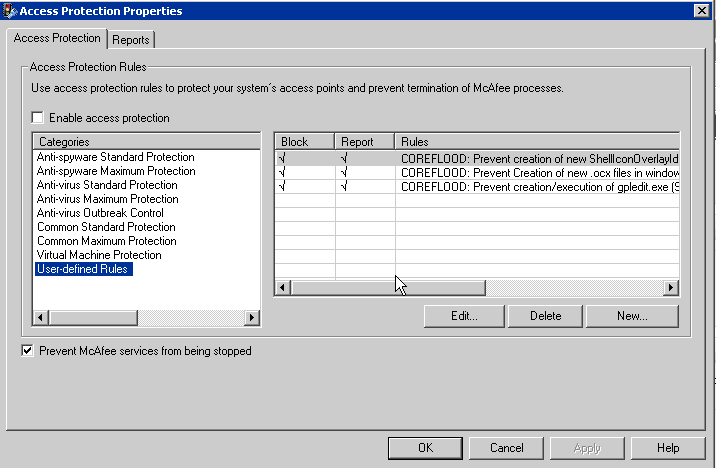
We then disabled the "Access Protection rule" and tried creating a new key on the same registry location. We were able to create it. Then we tried installing the NFS role services and this time it was installed successfully.
File Name Translation revisited
I had discussed on using File Name Translation over NFS here. Some additional information and an alternative steps is captured in this post.
To start with the characters that are supported by Windows are here: https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa365247%28VS.85%29.aspx
The lists of invalid / reserved characters are:
- < (less than)
- > (greater than)
- : (colon)
- " (double quote)
- / (forward slash)
- \ (backslash)
- | (vertical bar or pipe)
- ? (question mark)
- * (asterisk)
On the other hand the only characters not allowed in a filename in *nix are "NULL" and "/"
Enabling File Name Character Translation is discussed here: https://support.microsoft.com/kb/289627
Few important things to remember here is : Windows and UNIX operating systems have restrictions on valid characters that can be used in a file name. The list of illegal characters for each operating system, however, is different. For example, a UNIX file name can use a colon (:), but a Windows file name cannot use a colon (:). If a UNIX user attempts to create a file with a Windows illegal character on a Windows Services for UNIX network file system (NFS) share, the attempt is unsuccessful and the UNIX client computer receives an input or output error.
To work around this issue, use file name character mapping to replace characters that are not legal.
To enable file name character mapping, we need to create a character translation file and add a registry entry (one of the ways); another is using NFS management console.
A file name character translation file is a text file with a list of mapped characters in the following format where nn is the hexadecimal value of a single-byte character or one byte of a double-byte character, and comment is an optional comment:
0xnn[ 0xnn] : 0xnn[ 0xnn] [ ; comment]
* A single-byte character can be mapped to another single-byte character or to a double-byte character.
* A double-byte character can be mapped to another double-byte character or to a single-byte character.
* A semicolon (;) in the map file indicates a comment. Everything from the semicolon (;) to the end of the line is ignored.
The first character in the entry is the character on the (UNIX) client and the second is the character used on the Windows-based Server for NFS computer.
For example, the following maps the UNIX colon (:) to a Windows dash (-):
0x3a : 0x2d ; replace client : with - on server
Hexadecimal values can be easily obtained by using the Character Map utility that comes with Windows. Open Character Map and select a character. In the bottom left corner of the program, the character code displays the hexadecimal value of the character.
When we have created the file name character translation file, we must specify its name location in the system registry. To register the path and name of the file:
1.Use Registry Editor to locate this registry key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Server For NFS\CurrentVersion\Mapping
2.Edit the CharacterTranslation (REG_SZ) value.
3.Enter the fully qualified path name of the file name character translation file. For example, C:\Sfu\CTrans.txt.
Most importantly, we cannot replace a valid character in Windows using this.
Getting error "Network path Not found" after running dir command from Windows NFS client
While working on an access issue on Windows NFS clients, we found out that the 'dir' command does not work for a share which is exported through smb and NFS both. Once we run the dir command against the NFS share, it expects the share to be SMB and tries to access via smb protocol and not NFS.
Even pushing the NFS to the top of the Network provider list and restarting the client for NFS service, we could see the same issue.
The NFS client was Windows 2003 R2 and the NFS server was Solaris 10. Running the showmount against the Solaris server we could see multiple NFS shares. One of the share was a NFS export only and other was NFS + SMB export.
We ran the below command on both the shares from Windows client:
To make things clear collected netmon traces for working and non-working condition. For non-working there were no NFS packet and for working there were multiple NFS packet.
We suggested the following workaround for this:
- Have a share which is exported via NFS only.
- From the Korn shell 'ls' command against the NFS+SMB share and it worked.
- Also the start command from the command prompt worked.
Even though the 'dir' command gives an error, but rest all commands works on the NFS+SMB share. Also there is no issues mounting and accessing the NFS share.
Popular posts from this blog
[Excel] 문서에 오류가 있는지 확인하는 방법 Excel 문서를 편집하는 도중에 "셀 서식이 너무 많습니다." 메시지가 나오면서 서식을 더 이상 추가할 수 없거나, 문서의 크기가 예상보다 너무 클 때 , 특정 이름이 이미 있다는 메시지가 나오면서 '이름 충돌' 메시지가 계속 나올 때 가 있을 것입니다. 문서에 오류가 있는지 확인하는 방법에 대해서 설명합니다. ※ 문서를 수정하기 전에 수정 과정에서 데이터가 손실될 가능성이 있으므로 백업 본을 하나 만들어 놓습니다. 현상 및 원인 "셀 서식이 너무 많습니다." Excel의 Workbook은 97-2003 버전의 경우 약 4,000개 2007 버전의 경우 약 64,000개 의 서로 다른 셀 서식 조합을 가질 수 있습니다. 셀 서식 조합이라는 것은 글꼴 서식(예- 글꼴 종류, 크기, 기울임, 굵은 글꼴, 밑줄 등)이나 괘선(괘선의 위치, 색상 등), 무늬나 음영, 표시 형식, 맞춤, 셀 보호 등 을 포함합니다. Excel 2007에서는 1,024개의 전역 글꼴 종류를 사용할 수 있고 통합 문서당 512개까지 사용할 수 있습니다. 따라서 셀 서식 조합의 개수 제한을 초과한 경우에는 "셀 서식이 너무 많습니다." 메시지가 발생하는 것입니다. 그러나 대부분의 경우, 사용자가 직접 넣은 서식으로 개수 제한을 초과하는 경우는 드뭅니다. 셀 서식이 개수 제한을 넘도록 자동으로 서식을 추가해 주는 Laroux나 Pldt 같은 매크로 바이러스 에 감염이 되었거나, 매크로 바이러스에 감염이 되었던 문서의 시트를 [시트 이동/복사]하여 가져온 경우 시트의 서식, 스타일이 옮겨와 문제가 될 수 있습니다. "셀 서식이 너무 많습니다." 메시지가 발생하지 않도록 하기 위한 예방법 글꼴(종류, 크기, 색, 굵기, 기울임, 밑줄), 셀 채우기 색, 행 높이, 열 너비, 테두리(선 종류, ...
ASP.NET AJAX RC 1 is here! Download now
Moving on with WebParticles 1 Deploying to the _app_bin folder This post adds to Tony Rabun's post "WebParticles: Developing and Using Web User Controls WebParts in Microsoft Office SharePoint Server 2007" . In the original post, the web part DLLs are deployed in the GAC. During the development period, this could become a bit of a pain as you will be doing numerous compile, deploy then test cycles. Putting the DLLs in the _app_bin folder of the SharePoint web application makes things a bit easier. Make sure the web part class that load the user control has the GUID attribute and the constructor sets the export mode to all. Figure 1 - The web part class 2. Add the AllowPartiallyTrustedCallers Attribute to the AssemblyInfo.cs file of the web part project and all other DLL projects it is referencing. Figure 2 - Marking the assembly with AllowPartiallyTrustedCallers attribute 3. Copy all the DLLs from the bin folder of the web part...
Architecture Testing Guide Released
视频教程和截图:Windows8.1 Update 1 [原文发表地址] : Video Tutorial and Screenshots: Windows 8.1 Update 1 [原文发表时间] : 4/3/2014 我有一个私人的MSDN账户,所以我第一时间下载安装了Windows8.1 Update,在未来的几周内他将会慢慢的被公诸于世。 这会是最终的版本吗?它只是一项显著的改进而已。我在用X1碳触摸屏的笔记本电脑,虽然他有一个触摸屏,但我经常用的却是鼠标和键盘。在Store应用程序(全屏)和桌面程序之间来回切换让我感到很惬意,但总是会有一点瑕疵。你正在跨越两个世界。我想要生活在统一的世界,而这个Windows的更新以统一的度量方式将他们二者合并到一起,这就意味着当我使用我的电脑的时候会非常流畅。 我刚刚公开了一个全新的5分钟长YouTube视频,它可以带你参观一下一些新功能。 https://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=player_embedded&v=BcW8wu0Qnew#t=0 在你升级完成之后,你会立刻注意到Windows Store-一个全屏的应用程序,请注意它是固定在你的桌面的任务栏上。现在你也可以把任何的应用程序固定到你的任务栏上。 甚至更好,你可以右键关闭它们,就像以前一样: 像Xbox Music这种使用媒体控件的Windows Store应用程序也能获得类似于任务栏按钮内嵌媒体控件的任务栏功能增强。在这里,当我在桌面的时候,我可以控制Windows Store里面的音乐。当你按音量键的时候,通用音乐的控件也会弹出来。 现在开始界面上会有一个电源按钮和搜索键 如果你用鼠标右键单击一个固定的磁片形图标(或按Shift+F10),你将会看到熟悉的菜单,通过菜单你可以改变大小,固定到任务栏等等。 还添加了一些不错的功能和微妙变化,这对经常出差的我来说非常棒。我现在可以管理我已知的Wi-Fi网络了,这在Win7里面是被去掉了或是隐藏了,以至于我曾经写了一个实用的 管理无线网络程序 。好了,现在它又可用了。 你可以将鼠标移至Windows Store应用程序的顶部,一个小标题栏会出现。单击标题栏的左边,然后你就可以...




































Comments
Post a Comment